Both the J63A and J30J series connectors are high-reliability micro-rectangular connectors equipped with twisted wire spring contacts. Boasting exceptional vibration and shock resistance, they are widely utilized in high-end fields such as military electronics, aerospace, and precision instruments. However, significant differences exist between the two in terms of standard systems, structural design, performance parameters, and application scenarios, which directly determine the selection direction for different use cases.
From the perspective of standard systems and basic specifications, the two connectors adhere to entirely distinct technical standards. The J63A complies with GJB7245 (equivalent to MIL‑DTL‑32139A), featuring an ultra-narrow contact pitch of 0.635mm×0.635mm. This design reduces its volume to only 50% of the J30J, with a contact count ranging from 9 to 69 cores, making it the preferred solution for ultra-miniaturized and high-density interconnection scenarios. In contrast, the J30J is designed in accordance with GJB2446A (equivalent to MIL‑DTL‑83513), adopting a standard contact pitch of 1.27mm×1.27mm. It offers a more extensive range of contact counts (up to 144 cores) and higher versatility, capable of adapting to diverse connection requirements. Notably, due to differences in pitch and positioning structures, the two series are not directly interoperable, and customized adapter assemblies are required for system docking.
Differences in electrical and mechanical performance further delineate the application boundaries of the two products. In terms of electrical performance, the J30J delivers a rated current of 3A, an insulation withstand voltage of 800V, and a contact resistance of ≤20mΩ, meeting the demands of medium-power signal transmission and high-voltage isolation. The J63A, with a rated current of 1A and an insulation withstand voltage of 250V, is more suitable for high-density transmission of low-power consumption and small signals. Regarding mechanical performance, the J30J supports up to 500 mating cycles, making it suitable for working conditions requiring frequent insertion and extraction. The J63A, with a mating cycle of approximately 200 times, is better suited for fixed-installation and low-maintenance systems.
In terms of scenario adaptation, the positioning differences between the two connectors are particularly prominent. Leveraging its ultra-high density and lightweight advantages, the J63A has become a core component in medical equipment, portable precision instruments, and high-density PCB interconnections, enabling the integration of more signal channels within limited spaces. The J30J, with its superior power-carrying capacity and contact stability, is widely applied in aerospace onboard equipment, military measurement and control systems, and board-to-wire interconnections—fields with stringent requirements for reliability and durability.
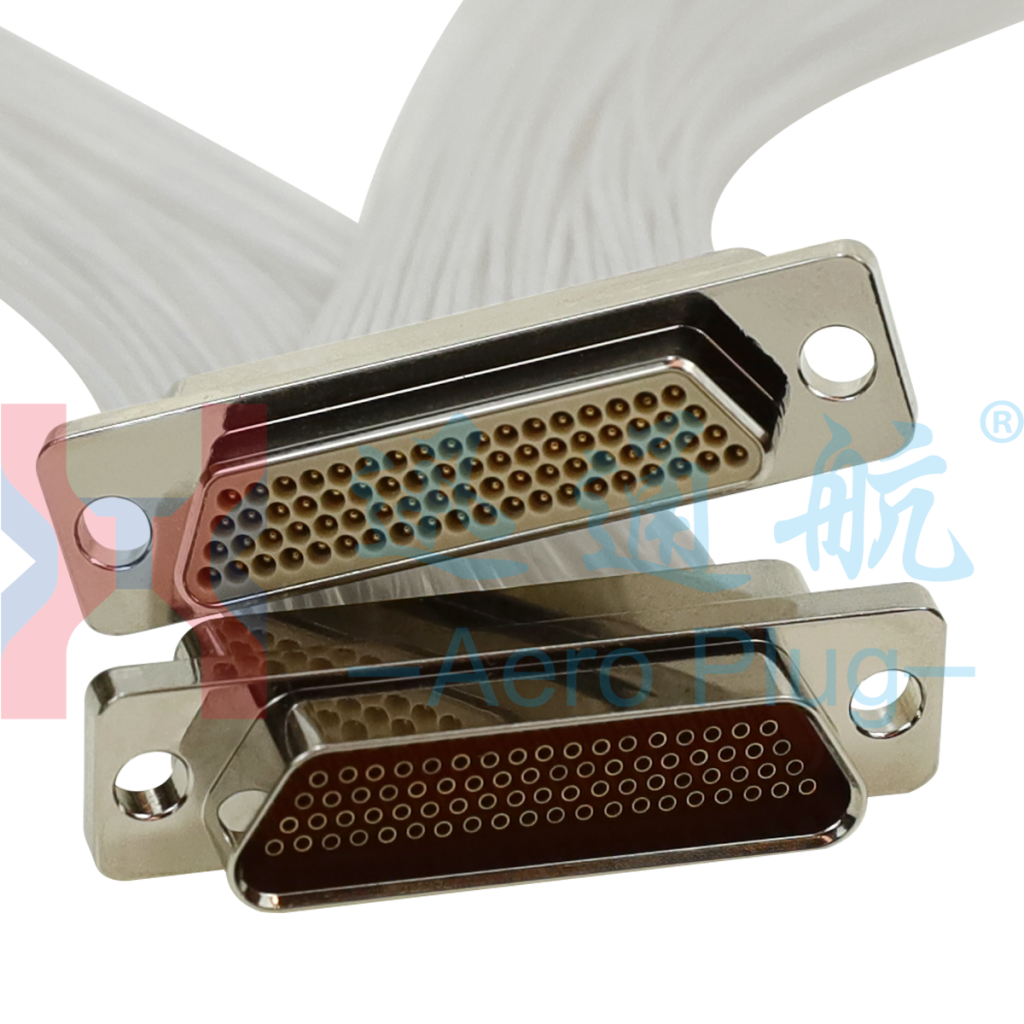

In summary, the selection of the two connectors should be based on core factors such as system space constraints, power requirements, and mating frequency. Only by accurately matching parameters with application scenarios can the stable operation of the system be guaranteed.

.png)
-1.png)